- Services
- Metals (overview)
- Plastics (overview)
- CAD Design
- Rapid Prototyping
& Rapid Tooling - CNC Machining
- Finishing & Assembly
- Rubber Plaster Molding
- Precision Airset Sand Casting
- Graphite Mold Die Casting
- One-Shot Casting
- Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
- Rapid Injection Molding
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Technical Information: One-Shot Casting Process
Download the PDF version of this document
What is One-Shot Casting?
Plaster mold casting is a method of producing aluminum, zinc or magnesium castings by pouring liquid metal into plaster (gypsum) molds. At Armstrong RM, there are two methods of plaster mold casting:
- Rubber Plaster Molding (RPM): Patterns create foundry tooling that makes copes, drags and core boxes used to create the plaster molds.
- One-Shot Casting: Plaster is poured directly on patterns, which are melted out in a furnace cycle.
Following is the process for the One-Shot method of making plaster mold castings.
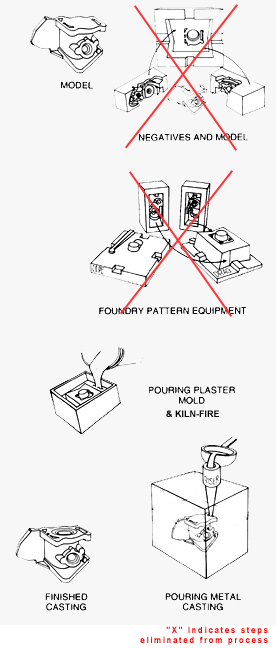
Step 1: Model/Pattern
- Constructed from customer drawing or CAD file.
- Laser-sintered patterns are produced.
- Model is engineered to include:
A) Metal shrinkage.
B) Mold taper (if required)
C) Machine stock (if required). - We can "clone" or adapt customer supplied model if requested.
Step 2: Plaster Mold
- A liquid plaster slurry is poured around the pattern.
- The plaster mold is heated in a furnace to melt out the pattern and cure plaster.
Step 3: Pour Casting
- Molten metal is prepared by degassing, and a spectrographic sample is taken to check the chemical analysis.
- The molten metal is then poured into the plaster mold.
- The plaster is removed by mechanical knock-out and high pressure waterjet.
- When the casting has cooled, the gates and risers are then removed.
Step 4: Secondary Operations
- The raw castings are inspected and serialized.
- Castings may then require (per customer specifications):
A) Heat treatment
B) X-Ray
C) Penetrant inspection - After finish inspection, casting is ready for:
A) Machining
B) Chemical film, chromate conversion, paint
or special finishes
C) Assembly
D) Form-in-place gasketing.
Download the PDF version of this document




